Science cluster

Summary
Earth Observation (EO) data is crucial for monitoring environmental changes, but its potential is often underutilised due to challenges in integrating advanced AI techniques. The FAIR-EO project aims to bridge this gap by making EO data more accessible and AI-ready, fostering innovation across both fields. Through the creation of AI4EOhub, a comprehensive and accessible repository of annotated datasets, AI models, and analysis pipelines, the project will enhance data discovery, preparation, analysis, and reproducibility. By aligning with FAIR principles, FAIR-EO supports global initiatives for sustainable and collaborative research, driving forward the application of AI in environmental and geospatial sciences.
Challenge
Open Science project
The AI and EO communities often struggle with data fragmentation, lack of standardisation, and barriers to collaboration. Data discovery, preparation, and the reproducibility of experiments are particularly difficult due to the absence of accessible, well-documented repositories. Additionally, EO data lacks comprehensive FAIR adherence, limiting its potential for AI applications and hindering cross-domain innovation.
Solution
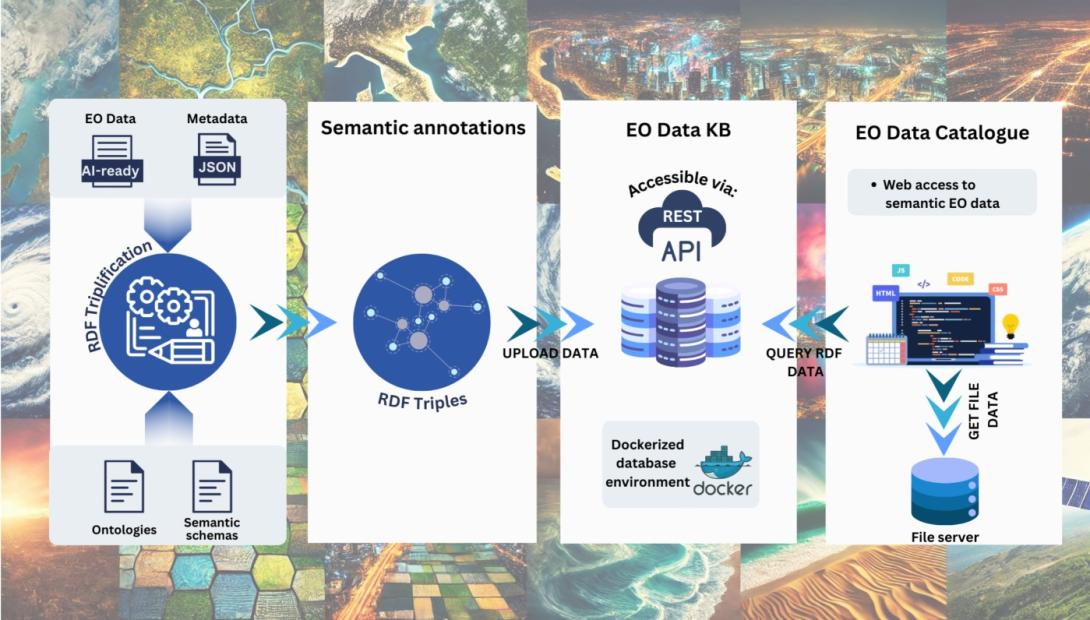
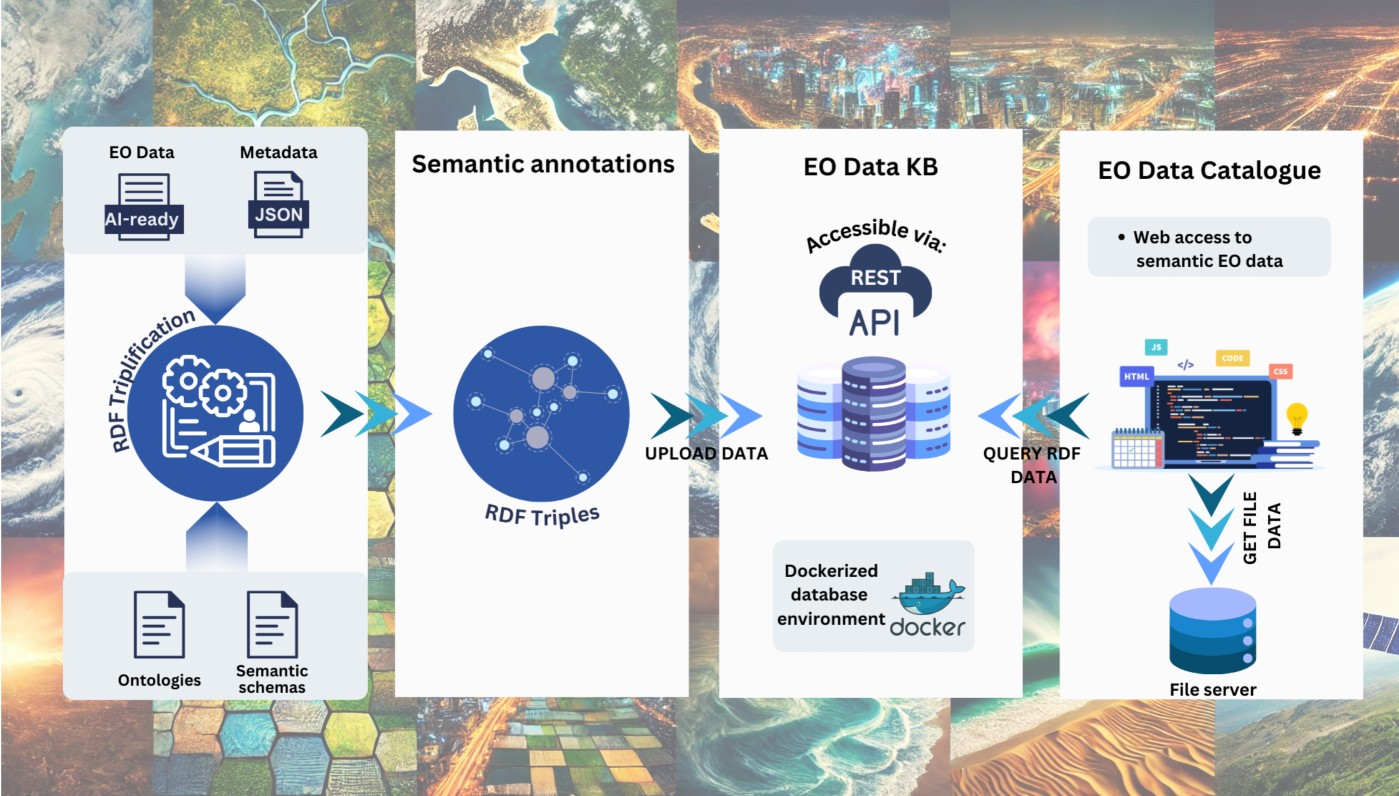
FAIR-EO aims to establish AI4EOhub, an integrated repository providing preprocessed, standardised, and annotated EO datasets optimised for AI applications, alongside standard AI methods and pre-trained models. A key innovation is the ontology-based schema for the semantic annotation of EO data, deep learning models, pipelines and results, enhancing their description, organisation, and interoperability for broader applications. AI4EOhub will house several key components designed to streamline the use of EO data in AI applications: a DataHub with annotated EO datasets, a ModelHub with AI methods and pre-trained models and their performance metrics, a PipelinesHub for ready-to-use analysis pipelines, and a ResultsHub for performance metrics and results from various models applied to a wide range of EO datasets. Moreover, the knowledge base will be populated with the semantically annotated experimental datasets, models, pipelines and results. Finally, AI4EOExplorer, a web-based interface, will make it easy for users to interact with AI4EOhub resources.
Scientific Impact
By promoting resource reuse and avoiding repetitive experiments, FAIR-EO supports sustainable research practices, aligning with the 'Green AI' initiative. It encourages interdisciplinary research and develops an interoperable semantic annotation schema to enhance data, AI model, and pipeline description and organisation. Emphasising interoperability with existing platforms and tools, it fosters cohesive and efficient data (re-)use. AI4EOhub will provide FAIR and AI-ready EO resources, setting a new standard for machine learning in EO. By bridging the gap between the EO and AI communities, it will significantly enhance the application of these technologies across scientific disciplines.
Results
- Developed and deployed DataHub: DataHub is a collection of processed, standardized and semantically annotated Earth observation (EO) datasets ready for use with artificial intelligence (AI). DataHub is accessible via a user-friendly web interface providing open access to all resources. The web interface is available here: https://eodata.bvlabs.ai/ai4eo/. Currently, there are 177 datasets available in DataHub.
- Gathered user feedback and defined user needs/requirements: The team gathered feedback from users working within key fields (Earth observation, artificial intelligence). Feedback was collected during a presentation at the Geospatial information technologies for resilient and sustainable society (GeoAI) project kick-off meeting with an engaging Slido poll (https://app.sli.do/event/pCVJ8gtb2fLLuqbhFTSUUu) and after the presentation with a Google Forms poll. A total of 23 participants engaged in a Slido poll and 7 users responded to the Google Forms poll. Our findings show that most users require time-series datasets for their work, and they generally work with multiple data sources simultaneously. Also, they are most interested in change detection tasks.
Events
- 3-4 March 2025 | Rome, Italy - 1st OSCARS Annual General Meeting | Presentation
- 18 November 2025 | Ljubljana, Slovenia - GeoAI project kickoff meeting. Presentation of the FAIR-EO project during the Geospatial information technologies for resilient and sustainable society (GeoAI) project kickoff meeting, where key stakeholders from the fields of Earth observation, artificial intelligence and visualisation were engaged and asked for feedback about the AI4EO platform | PRESENTATION, Poll (Slido).
- 20-21 November 2025 | Ljubljana, Slovenia - FAIR-EO project presentation at Open Science Day 2025, as part of the session “Open Science: from policy to good practices.” | Presentation recording (in Slovenian), Slides (in Slovenian)
- 10-12 March 2026 - 2nd OSCARS Annual General Meeting
Other material
- VIDEO | PRESENTATION - Odprta znanost: FAIR, odprti in za umetno inteligenco pripravljeni viri opazovanja Zemlje (FAIR-EO) - Tadej Tomanič, Bias Variance Labs
- FAIR-EO PRESENTATION
Principal investigator

Dragi Kocev is the co-founder of Bias Variance Labs and an expert in developing AI-driven resources for Earth observation and space applications. He has led the development of key tools, including the AiTLAS toolbox for Earth observation data analysis, the GalaxAI toolbox for spacecraft monitoring, and FAIR multi-label classification resources. Dragi has led multiple projects with the European Space Agency, such as AiSTRA, AiTLAS, and GalaxAI, and co-coordinated the MAESTRA project, thus advancing AI and machine learning techniques for structured data in Earth observation and space missions.